FTP vs SFTP: What's the Difference?
If you've ever needed to upload or download files from a server, you've probably come across FTP or SFTP. While both serve the same basic function -transferring files between computers- they differ significantly in terms of security and functionality. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone managing websites, servers or cloud storage solutions.
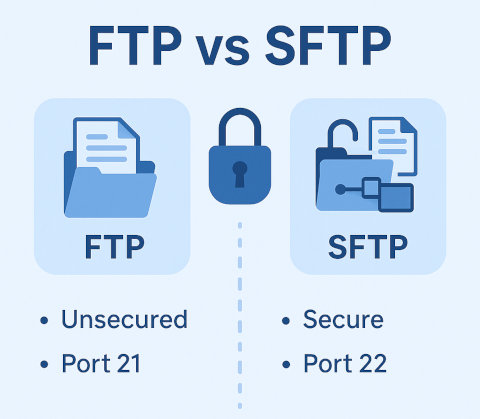
Let's start with explaining what FTP is.
What is FTP?
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. It's one of the oldest protocols used to transfer files between a client and a server over a network. FTP allows you to upload, download, rename, delete and manage files on remote servers.
However, FTP is inherently insecure. It transmits data including usernames and passwords in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and attacks. That's why it is not suitable when a secure connection is required.
Key Features of FTP
- Simplicity: Easy to use and widely supported.
- Multiple File Operations: Supports file uploads, downloads, renaming and deletions.
- Unauthenticated Option: Can be set up without user authentication (anonymous FTP).
What is SFTP?
SFTP stands for SSH File Transfer Protocol or Secure File Transfer Protocol. Unlike FTP, SFTP encrypts the data being transferred, including credentials and file contents, by using the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol.
This encryption makes SFTP a much more secure choice for transferring sensitive or private data over the internet.
Key Features of SFTP
- Encryption: All communications are encrypted, including passwords and data.
- Firewall Friendly: Operates over a single port (usually port 22), making it easier to manage through firewalls.
- Authentication: Supports password, public key, or multi-factor authentication.
- File Permissions: Allows for advanced user permission settings.
Main Differences Between FTP and SFTP
Now, let's see the differences in FTP and SFTP on a comparison table.
| Feature | FTP | SFTP |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Unencrypted | Encrypted via SSH |
| Port Used | Ports 20 & 21 | Port 22 |
| Authentication | Basic username/password | Username/password or SSH keys |
| Data Protection | None | Encrypted during transfer |
| Firewall Compatibility | Can be tricky with multiple ports | Better with single port |
When to Use FTP
You might consider FTP in the following scenarios:
- When transferring non-sensitive data within a trusted network.
- When connecting to legacy systems or older servers.
- When encryption is not a requirement.
When to Use SFTP
SFTP is a better choice in most modern environments, especially when:
- Handling confidential or sensitive data.
- Transferring files over public or unsecured networks.
- Compliance with data security regulations is required.
- You need stronger authentication mechanisms.
How to Choose Between FTP and SFTP
The choice between FTP and SFTP largely depends on your use case and security needs. If you're managing sensitive information or require regulatory compliance (such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc.), SFTP is the safer and more modern protocol. For simple, internal tasks where speed and simplicity are more important than security, FTP may still have a place.
Understanding the difference between FTP and SFTP helps ensure your file transfers are secure and appropriate for your workflow. As cybersecurity becomes increasingly important, choosing encrypted protocols like SFTP is generally the smarter decision.
